How can you maintain both altitude and airspeed during a turn?
In a banked turn, the total lift remains constant, but it is divided into two components: one vertical and one horizontal. The vertical component of lift becomes smaller as the bank angle increases, which would normally cause a descent.
To maintain altitude, the angle of attack must be increased to restore the vertical lift component to match the aircraft’s weight. However, increasing the angle of attack also increases drag and may reduce airspeed.
To counter this, additional thrust is required to maintain airspeed while sustaining the turn.

Note: During a level turn, the total lift must be greater than the aircraft’s weight in order to maintain a vertical lift component equal to the weight. As a result, the load factor exceeds 1 G, since Load Factor = Lift / Weight.
Define the difference between Mcrit and MMO.
Mcrit (critical Mach number) is the lowest Mach number at which airflow over any part of the aircraft — typically the wing — first reaches Mach 1, leading to the onset of compressibility effects such as shock waves, drag rise, and flow separation.
MMO (Maximum Mach Operating number) is the maximum authorized Mach number for safe operation of the aircraft. It ensures that the aircraft remains below speeds that could cause structural stress, control issues, or high-speed buffet.
In summary:
- Mcrit marks the start of transonic effects
- MMO is a design limitation to avoid unsafe flight conditions
- Mcrit is always lower than MMO
Flying beyond MMO may result in loss of control or airframe damage, and must be avoided.
What are the two main types of aerodynamic drag?
The two primary types of aerodynamic drag acting on an aircraft are:
- Parasite drag: Caused by the aircraft moving through the air. It includes form drag, skin friction, and interference drag. Parasite drag increases with the square of airspeed.
- Induced drag: Also called lift-induced drag, it results from the generation of lift. It is highest at low speeds and decreases as speed increases.
Total drag is the sum of both:
Total Drag = Parasite Drag + Induced Drag

Define critical angle of attack.
The critical angle of attack is the angle above which aerodynamic stall occurs. At this point, the airflow can no longer remain attached to the upper surface of the wing, leading to a rapid loss of lift.
At the critical angle, the lift coefficient (CL) reaches its maximum. Beyond this point, even if the angle of attack increases, the wing can no longer generate sufficient lift to sustain flight.

Note:
- Every aircraft stalls at a specific angle of attack for a given configuration — not at a specific airspeed or attitude.
- The critical angle of attack decreases at high altitude and high Mach numbers due to compressibility effects and aerodynamic limits.
- Airframe icing can also lower the critical angle of attack significantly.
- Wing configuration affects it as well:
- Leading-edge slats and flaps, when extended, tend to increase the critical angle of attack.
- Trailing-edge flaps, on the other hand, generally reduce it.
- For this reason, in most jet aircraft, leading-edge devices extend automatically when trailing-edge flaps are deployed.
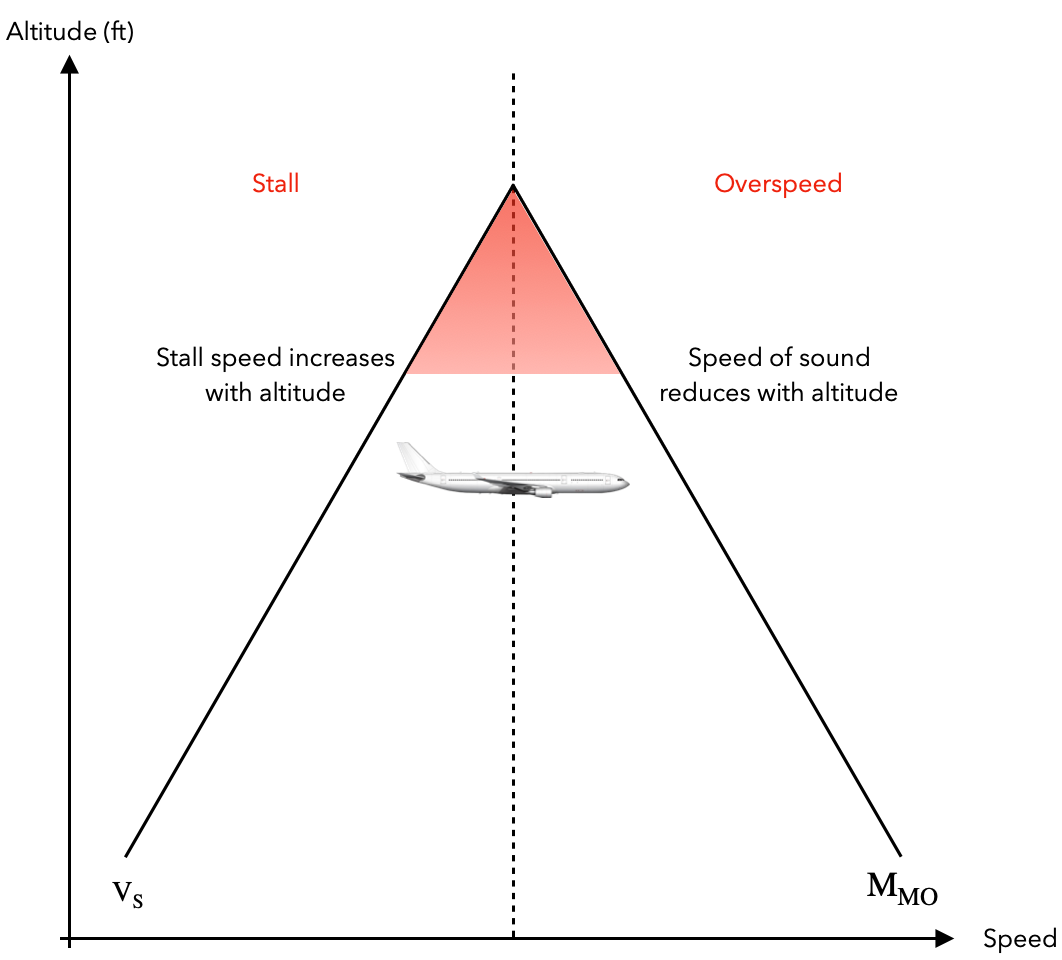
How is the term “coffin corner” defined in high-altitude jet operations?
Coffin corner is the altitude at which the aircraft’s stall speed equals its maximum operating speed.
At this point, any decrease in speed will cause a low-speed stall due to airflow separation when the critical angle of attack is exceeded.
On the other hand, any increase in speed will lead to a high-speed stall because airflow deceleration occurs due to shock waves forming on the aircraft’s wings.
 Some questions are reserved for members only. Log in or sign-up below to access the full content.
Some questions are reserved for members only. Log in or sign-up below to access the full content.Cruise
6.25€/month
- Access to selected Q&A
- All technical questions
- All non-technical questions
- All type-specific questions
- Access exclusive articles
- No automatic renewal
- Access for 12 months
Climb
8.75€/month
- Access to selected Q&A
- All technical questions
- All non-technical questions
- All type-specific questions
- –
- No automatic renewal
- Access for 8 months
Take-off
15€/month
- Access to selected Q&A
- All technical questions
- All non-technical questions
- –
- –
- No automatic renewal
- Access for 4 months
Taxi
20€/month
- Access to selected Q&A
- All technical questions
- All non-technical questions
- –
- –
- No automatic renewal
- Access for 1 month